Pediatric ENT
We specialize in providing the best care to children of all ages. Common problems in this age group are –

1. Tonsil and Adenoid Disease
At our hospital we follow a conservative approach in treating children as per international guidelines. We recommend removal of tonsils and adenoids if the child has developed recurrent attacks of infection.
The ABOTO guidelines for Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are-
More than 7 attacks of infection per year in one year.
More than 5 attacks of infection per year in 2 years or
More than 3 attacks of infection per year in 3 years.
We follow this 7-5-3 rule. Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy is performed using a latest technique called coblation. This results into bloodless surgery, minimal pain and same day discharge.

Smith and Nephew Coblator Console and wand
2. Chronic Ear Infection
The same 7-5-3 rule is applied for treatment of chronic ear infections in children. Myringotomy or ventilating tube is only inserted if fluid persists for more than 3 months leading to conductive hearing loss. Most ear infections are caused due to chronic nasal allergies leading to eustachian tube dysfunction
3. Hearing loss
Congenital hearing loss (hearing loss since birth) is either sensorineural or conductive in nature. We offer a simple, objective hearing test in children called OAE. Otoacoustic emission (OAE) test detects the emissions directly from the inner ear once a stimulus is placed. We use MAICO ERO-SCAN DP (Distortion Product) OAE Screener for this purpose.
For children more than 2 years of age sound field audiometry can be performed whereas for child more than 4 years of age, pure tone audiometry can be performed, just like adults to determine the type of hearing loss. If a child has congenital SNHL an extensive work up is performed that consists of urine analysis, EKG to rule out Jervell-Neilson syndrome, thyroid function test (TFT) to rule out Pendred syndrome and CT temporal bone to evaluate structural abnormality in inner ear. Amplification (hearing aids) is then offered as soon as possible. However we do not perform cochlear implantation at our hospital.
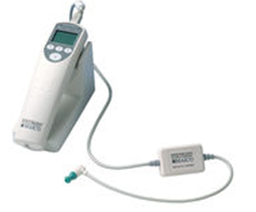
ERO-SCAN DP (Distortion Product) OAE Screener
How Does This Hearing Loss Affect Your Child?
Hearing loss in children causes delay in speech and language development. In school, these children may not listen. Mild to moderate hearing loss can be missed by teachers as well as parents at home. This can result into educational defficulties and behavioral problems. So early detection of hearing loss is extremely important.
So early detection of hearing loss and amplification becomes extremely important.
4. Tongue Tie
It is a condition where the tongue is attached by a band to the floor of mouth, restricting mobility of the tongue. This may result into difficulties with speech or swallowing. It can easily be corrected by a procedure called frenulectomy (Release of tongue tie).
5. Epistaxis
The most common cause of bleeding from the nose in children is nose picking and dryness of inside lining of the nose. This can be addressed by providing moisture to the area, changing habits or even simple cauterization if necessary.
6.Congenital Neck Mass
The common conditions which cause neck swellings in childhood include thyroglossal duct cyst, branchial cysts, branchial fistulas etc
Failure of closure of tracts during development can lead to formation of cysts in the neck. They can be managed very well with appropriate surgery and cosmetically favorable minimal incisions.
7. Sinus Infection
In pediatric age group maximal medical treatment remains to be the mainstay of care to avoid surgery. However congenital disorders like cystic fibrosis need to be ruled out in children with nasal polyps.
8.Difficulty Breathing or Stridor
Common conditions which can cause breathing difficulties or noisy breathing in childhood are
Laryngomalacia –
A collapse of laryngeal cartilages above the vocal folds leads to breathing difficulties or noisy breathing. This is usually seen one mouth after birth in affected babies. Surgery is only indicated if patient turns blue (is not receiving enough oxygen) or is having difficulty feeding resulting into failure to thrive. But most patients do not need any surgical intervention.
Choanal Atersia –
It is an absence of opening from nose to mouth. The baby is unable to breathe through the nose. Newborns are obligate nasal breathers. Bilateral choanal atresia needs urgent surgical intervention. Unilateral can be operated at a later date.
